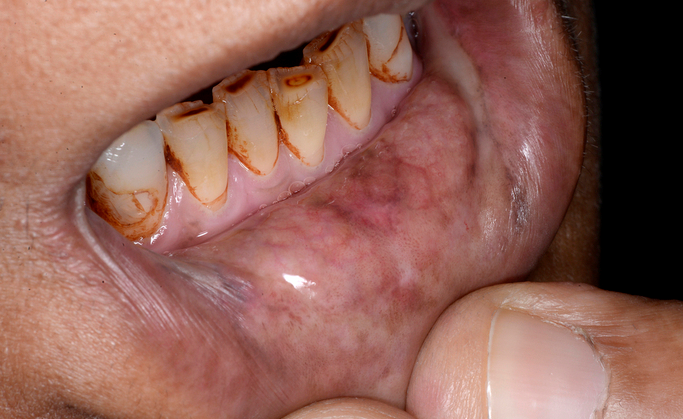
Oral Submucous Fibrosis
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSF) is a chronic, progressive condition that affects the tissues inside the mouth. It is characterized by the thickening and scarring (fibrosis) of the mucous membranes, leading to stiffness and a reduction in the mouth’s ability to move. This condition can make it difficult to open the mouth fully, affecting speaking, eating, and swallowing.
Symptoms:
- Thickening of the oral mucosa
- Difficulty in opening the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing or chewing
- A burning sensation in the mouth
- White or pale patches in the mouth etc.
Surgical Approach:
- Fiberotomy- The fibrous bands that limit mouth opening are surgically excised or released. This helps to improve the motion of the jaw, and allows the patient to open their mouth wider and improves oral functions like speaking and eating.
- Frenectomy- The frenulum, a small fold of tissue under the tongue or between the lips and gums, may be involved in restricting mouth movement. A frenectomy involves removing or loosening the frenulum to improve oral mobility.
- Buccal Mucosa Grafting- In cases where the mucosal lining is severely affected, grafts of healthy tissue can be used to replace damaged tissue. This is done to restore mouth functionality and improve comfort.
- Mandibular Osteotomy- In cases where Oral Submucous Fibrosis has caused significant restriction of jaw movement, osteotomy (surgical cutting of the bone) may be performed to improve jaw opening and functionality.



